The Intel® Processor Identification Utility was developed by Intel Corporation to identify characteristics of the processor inside a system.
In addition to displaying processor details, this tool provides a frequency test feature to determine if the processor is operating at the tested and rated speed marked on the processor.
The Intel Processor Identification Utility is consistently updated to support the latest processors developed by Intel. The supported processors page provides a complete list of processors currently supported by the tool. This page includes a table showing which processors are supported by this tool, and which processors are supported by the Intel® Processor Frequency ID Utility.
There are two versions of the utility available. The Windows* version of the utility can be used with systems that support the Windows operating system environment. The "Bootable" version of the utility does not require an operating system. By installing the tool on a bootable device (e.g. floppy drive) the tool is run as the system is booted, but before the operating system is loaded. This is normally done from a PC's floppy "A:" drive.
Download Now. . .
Sunday, January 23, 2011
Saturday, January 22, 2011
Friday, January 14, 2011
Enable Hibernate Option In Windows 7
If you are looking to hibernate windows 7 but cannot find the option, here’s a small tutorial that will enable the hibernate option. 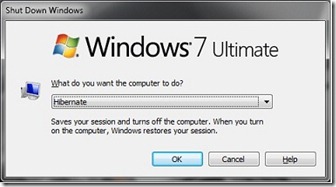

Read More . . .
Thursday, January 13, 2011
What Is Cloud Computing ?
From Microsoft Course 10324A
Cloud computing is a new virtualization option that enables organizations to
purchase IT services from Internet-based service providers or to provide IT services
through the Internet. These services can include servers, storage, or networking
resources. The services may be running on virtual environments based on Hyper-V
or one of the other virtualization options. The actual server and storage
deployment is largely transparent to the users who consume the services. They
typically are concerned only with being able to access their required applications
easily.
A cloud computing environment normally includes:
• A data center that contains virtualization hosts and storage. In the Microsoft
solution, these hosts are running Hyper-V.
• Virtual servers, storage and network resources located in the data center.
• A highly available and high bandwidth network connection to the Internet.
Automated processes and tools for deploying and configuring virtual
machines. These processes may be managed entirely by the online service
provider, or may be exposed to the customer to manage their own virtual
environment.
• Tools for managing the interaction of local and cloud computing. Many
organizations still host most IT services locally even as they begin to move
some services to the cloud. You can use this integration tool to ensure that
users can gain seamless access to both local and cloud resources. For example,
most organizations will still run Active Directory® Domain Services (AD DS)
locally. Ideally, users should be able to authenticate once to their local domain,
and gain access to all required services regardless of whether they are located
internally or in the cloud.
Cloud computing provides several benefits for organizations:
• Flexible deployment options. The organization may host the data center that
provides cloud services or an external hosting provider, such as Microsoft or a
third party, may host it.
• Scalability. In a cloud-computing scenario, all service components are virtual,
which makes it very easy to scale up or down, as necessary. For example, if an
organization requires more resources, it can deploy additional virtual
machines in the data center. If the organization requires fewer resources, it can
save money by removing virtual machines or by reusing the physical resources
for another purpose.
• Potential for decreased cost. By purchasing online services from a hosting
provider, organizations often can implement services for a cost that is
significantly less than hosting the services locally.
• More reliable and effective services. Some services require constant monitoring
and specialized skills. By purchasing these services from an online service
provider, organizations can take advantage of the infrastructure and skills that
are available at the hosting provider, but which may be prohibitively expensive
for a small organization.
From Microsoft Course 10324A
Cloud computing is a new virtualization option that enables organizations to
purchase IT services from Internet-based service providers or to provide IT services
through the Internet. These services can include servers, storage, or networking
resources. The services may be running on virtual environments based on Hyper-V
or one of the other virtualization options. The actual server and storage
deployment is largely transparent to the users who consume the services. They
typically are concerned only with being able to access their required applications
easily.
A cloud computing environment normally includes:
• A data center that contains virtualization hosts and storage. In the Microsoft
solution, these hosts are running Hyper-V.
• Virtual servers, storage and network resources located in the data center.
• A highly available and high bandwidth network connection to the Internet.
Automated processes and tools for deploying and configuring virtual
machines. These processes may be managed entirely by the online service
provider, or may be exposed to the customer to manage their own virtual
environment.
• Tools for managing the interaction of local and cloud computing. Many
organizations still host most IT services locally even as they begin to move
some services to the cloud. You can use this integration tool to ensure that
users can gain seamless access to both local and cloud resources. For example,
most organizations will still run Active Directory® Domain Services (AD DS)
locally. Ideally, users should be able to authenticate once to their local domain,
and gain access to all required services regardless of whether they are located
internally or in the cloud.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
• Flexible deployment options. The organization may host the data center that
provides cloud services or an external hosting provider, such as Microsoft or a
third party, may host it.
• Scalability. In a cloud-computing scenario, all service components are virtual,
which makes it very easy to scale up or down, as necessary. For example, if an
organization requires more resources, it can deploy additional virtual
machines in the data center. If the organization requires fewer resources, it can
save money by removing virtual machines or by reusing the physical resources
for another purpose.
• Potential for decreased cost. By purchasing online services from a hosting
provider, organizations often can implement services for a cost that is
significantly less than hosting the services locally.
• More reliable and effective services. Some services require constant monitoring
and specialized skills. By purchasing these services from an online service
provider, organizations can take advantage of the infrastructure and skills that
are available at the hosting provider, but which may be prohibitively expensive
for a small organization.
From Microsoft Course 10324A
Labels:
cloud,
cloud computing,
computing,
microsoft
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)